Antioxidants are often mentioned in daily conversation. You can find antioxidant supplements in shop racks, and their health and wellness advantages are cherished by both online marketers as well as media. Really, only a couple of individuals really recognize exactly what they are and how they function. They are thought to contribute in stopping the growth of such persistent illnesses as cancer cells, heart problems, strokes, Alzheimer’s illness, rheumatoid joint inflammation, cataracts and a lot more.
The idea of anti-oxidants is pretty hard to explain, but we will try to break it down in more simple terms.
What exactly are antioxidants?
Are they minerals, vitamins or enzymes?
They are all of the above yet cannot be classified as such; they are classified by what they do.
First and foremost, antioxidants are substances that are capable of countering the harmful, but normal, properties of the physiological process of oxidation in animal tissue. Antioxidants are both nutrients (vitamins and minerals) as well as enzymes (proteins in your body that assist in chemical reactions). They have always been around, long before the 21st century, and have been used as herbal remedies and natural medicine for a long time.
The prefix ‘anti’ means against, in opposition to, or corrective in nature. In this instance, the ‘anti’ in antioxidant describes the effect these chemicals have against oxidants.
Oxidants, usually referred to as ‘free radicals’, are produced as a natural by-product of the millions of biochemical processes undertaken by the body every minute. The same life-giving oxygen that supports all the functions of the body creates these harmful by-products which cause cell damage, usually to DNA, cell membrane, fats and proteins.
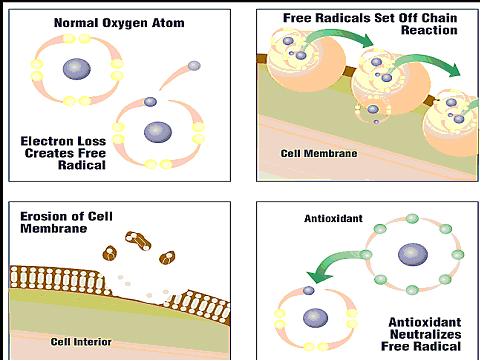
Antioxidants are nature’s way of defending your cells against attack by reactive oxygen species (ROS). When cells create energy in our body, they also produce unstable oxygen molecules. These molecules, called free radicals, have a missing electron. To be more specific, free radicals are chemically active atoms or molecular fragments that have a charge due to an excess or incomplete number of electrons.
Since they have one or more unpaired electrons, free radicals are highly unbalanced. They scavenge your body to grasp onto or donate electrons, thereby damaging cells, cell proteins, and DNA (genetic material).
The free radical bonds to healthy molecules stealing their electron, hence making the healthy cell into a free radical. Free radicals can have a snowballing effect in which molecule after molecule steals from its neighbor, each one becoming a new free radical once it’s been electron-robbed. It leaves a trail of biological carnage, as illustrated in the video below.

If the amount of free radical oxidation in the body is allowed to rise to an unhealthy level, it can result in extensive damage to cellular components and can therefore speed up the aging process.
It’s difficult to explain what antioxidants are without you learning a bit more about free radicals and how they cause oxidative damage. Read more….
Free radicals are very dangerous to the body’s tissues and have been linked to cancer and premature aging. The body uses antioxidants to protect itself from the damage inadvertently caused by excessive oxygen cells.
How Do Free Radicals Interact With Antioxidants?
An antioxidant is a molecule that hinders the oxidation of other molecules, helping to prevent certain kinds of cell damage. Antioxidants break the free radical chain of reactions by sacrificing their own electrons to feed free radicals, without becoming free radicals themselves. In essence, they are all electron donors.
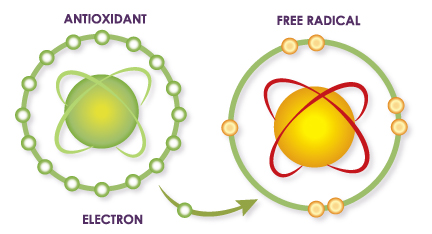
Antioxidants convert free radicals into non-damaging biochemical substances, hugely assisting with the reparation of cellular damage. The antioxidant nutrients themselves don’t become free radicals by donating an electron because they are stable in either form.
An antioxidant is not actually a substance; it is a behavior. Any compound that can donate electrons and counteract free radicals has antioxidant properties. Antioxidants prevent free radicals from oxidizing (removing electrons from) sensitive biological molecules.
It is actually an ongoing natural process, with oxidants “attacking” our cells in search of an electron and at the same time antioxidants providing the electron in order to lessen the damage. Antioxidants can simply be thought of as “electron donors”.
When you are getting enough antioxidants on a regular basis, you are providing your body with the necessary provisions and tools that it needs to avert disease and reverse damage. The human body naturally aims towards optimal health, but it is absolutely necessary to provide the vital building blocks in order to be healthy.
As the antioxidants are working in your body, they identify free radicals and neutralize them. Antioxidants also work to reverse the damage that has arisen from the free radicals.
Here are some compounds with antioxidant abilities
Alphacarotene Alphalipoic acid Lycopene
Astaxanthin Betacryptoxanthin Manganese
Carnitine Betacarotene Catalase
Catechins Coenzyme Q10 Flavonoids
Glutathione Melatonin Lutein & Zeaxanthin
Iridium Quercetin Phenols & Polyphenols
Selenium Resveratrol Phytoestrogens
Vitamin A Uric acid Superoxide dismutase
What Other Roles Do Antioxidants Play In Our Body?
Besides interrupting free radical raids and melting down toxic invaders, antioxidants have some other unique and interesting functions, such as:
- Repairing Damaged Molecules: A few unique antioxidants can repair a damaged molecule by donating a hydrogen atom—and this becomes imperative when the molecule is a critical one, like your DNA.
- Blocking Metal Radical Production (Chelating Effect): Toxic metals such as mercury and arsenic catalyze free radical production. Some antioxidants (such as green tea) have the ability to grab these metals and “hug” them so strongly that no chemical reaction can take place— this is called chelation. Water-soluble chelating agents also help to guide toxic metals out of your body in your urine.
- Stimulating Gene Expression and Endogenous Antioxidant Production: Some substances have a remarkable ability to stimulate your body’s genes to increase your natural defenses. Whey proteins are thought to do this, as does exercise.
- “Shield Effect”: The flavonoids attach themselves to your DNA and protect it from attack by free radicals, acting as a virtual shield.
- Cancer Cell Suicide Promoter: Some antioxidants boost anti-cancer chemicals, halting cancer growth and even forcing some cancer cells to self-destruct (apoptosis).
To summarize: Antioxidants have both a PREVENTION and CURE agenda. They provide different aid, at different stages of the oxidation process. They provide 3 levels of defense in our body:
- Protect the cells from oxidation process, at different stages of the oxidation process:
- Before the oxidation process can damage the cells (Level 1) With sufficient levels of antioxidants in the body, free radicals have lesser chance of getting near the cells to cause damage. And if they reach the cells, antioxidants can neutralize its damaging attacks before they can create any damage to the cells.
These antioxidants are usually the Enzymes antioxidants produced by the body, such as :
- Superoxide dismutase (SOD)
- Catalase
- Glutathione Peroxidase
However, the cells also rely on "external" antioxidants from food, water and if need be, supplements, such as:
- Vitamin A, C and E
- Lycopene
- Minerals, such as Selenium
- Hydrogen
- After the oxidation process already started, they can arrest the damage by either eliminating the Free Radicals or neutralizing the Free Radicals (Level 2) , and repairing whatever damages done. The basically clean up and repair after the damage assault has begun
- Repair the cells after the damage has been done (Level 3) and this way providing the Cure
When we do not have sufficient antioxidants in the body and when the damage has already been done, all is still not lost, as antioxidants have repair capabilities.
However, what can be repaired is dictated by the body or cells, not by antioxidant. They want to do their repair job but certain type of cells cannot be repaired. As we know today, once brain cells are damaged, we can no longer repair them. And some damages, if left for too long, may be beyond repair ...
As the old adage goes, “Prevention is BETTER than cure”, in which it would be best to ensure that we always have sufficient levels of antioxidants in the body.
You may also like:
Free Radicals: Enemies Within. What Are They And How Are They Formed
Classification Of The Anti-Oxidants



